The simplest and common way to do this would be by using the command:
tail -F $LOGFILEwhere $LOGFILE is an environment variable corresponding to the path to the log file to be monitored.
By default, the Linux tail command prints the last 10 lines of a file to standard output. The -F option causes additional file content to be displayed in real time as the file continues to grow. This yields a simple mechanism for monitoring services via their log files in close to real time.
Two other specific command line options of interest in this context are:
The -s option causes tail to sleep for a specified number of seconds between updates (e.g., ‘tail -F -s 10’ will update the displayed file contents roughly every 10 seconds rather than in close to real time as the file is updated).
The -n option can be used to specify a number of lines other than 10 to initially display (e.g., ‘tail -n 20 -F’ will first display the last 20 lines of the file and will then continue updating the output in realtime).
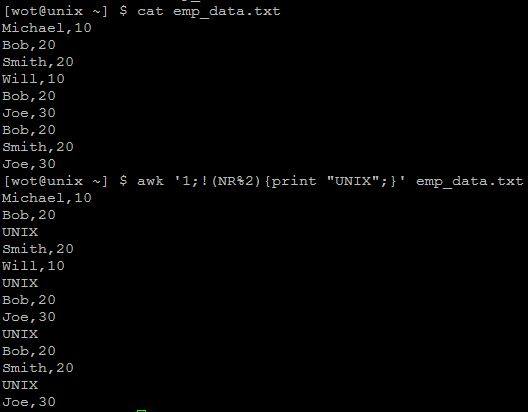
Let us consider a file. The requirement is to insert a line with text “UNIX” after every 2 lines. Below awk script can insert string “UNIX” in a file for each 2 lines.
$ awk '1;!(NR%2){print "UNIX";}' emp_data.txtOR
$ sed 'N;s/.*/&\nUNIX/' emp_data.txt
Read also: Unix interview questions and answers part – 1
$ dos2unix filenameOR
$ sed 's/^M//g' filename$ date -d "1 day"
Read also: Unix interview questions and answers part – 2
By using command “uname -a” in Unix$ uname -a
For running a process in background use “&” in command line.
For bringing it back in foreground use command “fg jobid” and for getting job id you use command “ps”, for killing that process find PID and use ‘kill -9 PID’ command.We have many options to transfer files from one host to another host, you can say by using “scp” command. You can also use rsync command to answer this or even sftp would be okay.
Read also: Unix interview questions and answers part – 3
By using “df” command in Unix. For example “df -h .” will list how full your current drive is.
$ cut -c -5 filename
$? gives the exit status of the last command that was executed.
0 (Zero) – means command returns successful.
Non Zero – means command returns unsuccessful.